Cultures
Diversity, technology and strategic planning are the guidelines that govern Cambuhy Agrícola’s business management, an operational model that aims for productivity and high quality in the cultivation of Orange and Sugarcane.

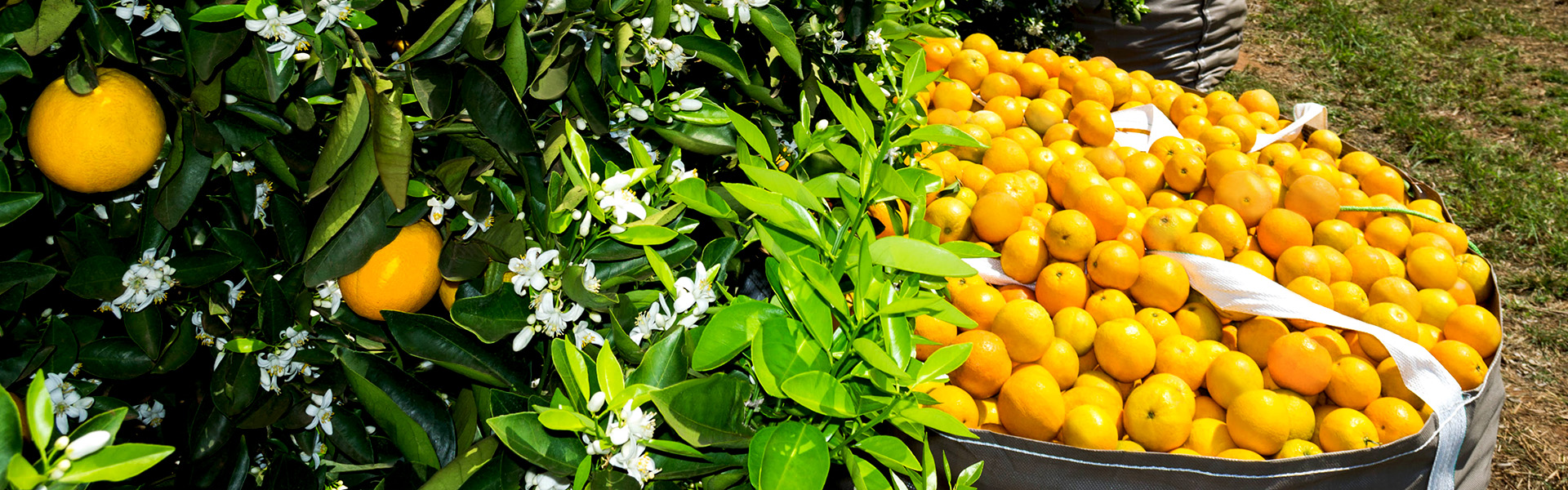
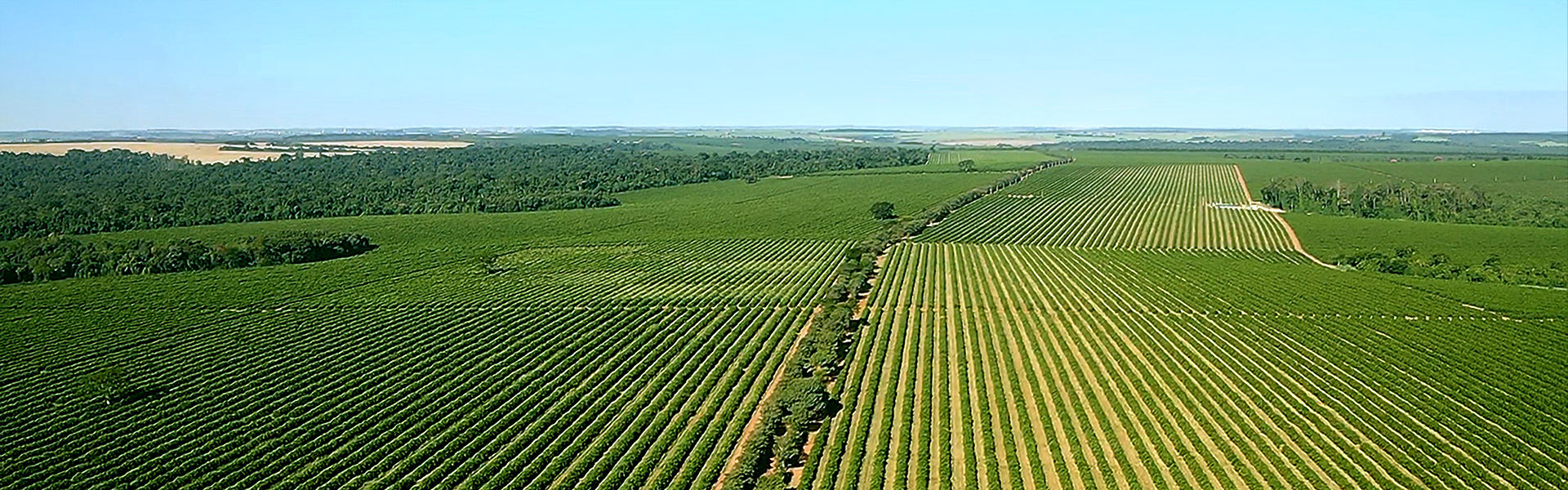
 Orange
Orange

TECHNOLOGY AND OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE AS THE FOUNDATION FOR HIGH YIELD
Cambuhy Agrícola is a benchmark company in the citrus sector for its good management practices and environmental concern.
Oranges are its main crop, occupying more than half of its arable area. Different varieties of orange are grown, including early varieties (Valencia Americana and Hamlin), a mid-season variety (Pera) and late varieties (Valencia, Natal and Folha Murcha). Swingle is the most commonly used rootstock.
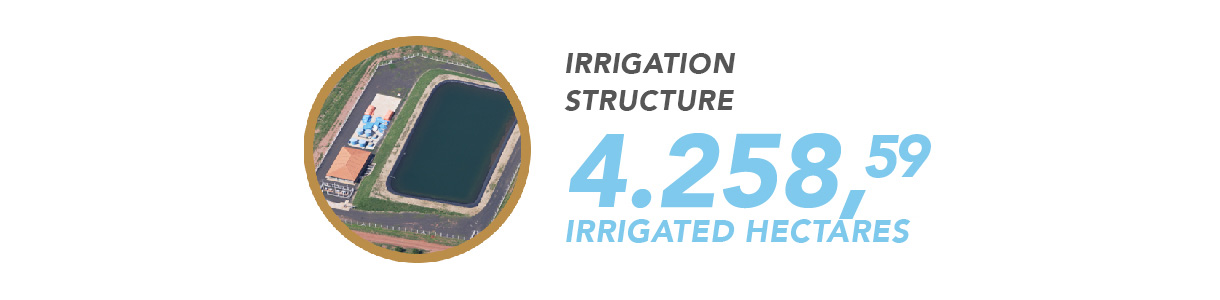
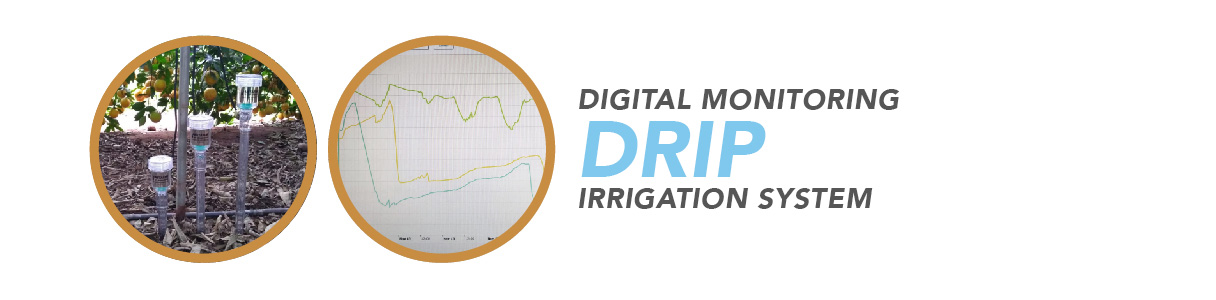
Cambuhy has more than 60 percent of its area under drip irrigation and consistently seeks new technologies, partnering with prominent companies and research institutions and focusing on constant updates on the best management methods to achieve quality and yield.
In recent years, Cambuhy has produced an average of five million boxes of oranges that were processed as juice and by-products. Cambuhy is focused on providing the market with a highly competitive cost and products of excellent quality.
MANAGEMENT
Cambuhy Agrícola carries out a rigorous crop management process, by implementing best practices, spraying specific to plant size and pest or disease, frequent scouting, annual pruning, eradication of infected plants, healthy nursery plants, etc., which makes Cambuhy highly competitive in a sector with substantial production costs. All these practices have established Cambuhy Agrícola as an international benchmark for being able to maintain high production and low disease rates.
REFERENCE IN GREENING MANAGEMENT
Cambuhy Agrícola adopts three control measures to manage citrus greening:
1) Internal management: adoption of rigorous processes that contribute to identifying and checking the epidemic within the orchard, such as monitoring the insect vector by using yellow traps, spraying, visual scouting, and eradication of infected trees.
2) Regional management: this type of management consists of holding technical alignment meetings with various producers in the region to coordinate simultaneous psyllid control measures, standardize spraying dates according to the monitoring of the vector in the region and implement other measures, leading to a reduction in citrus greening in the region.
3) External management: this is a complement to regional management, with Cambuhy being the pioneer in adopting this practice. It consists of mapping abandoned and non-commercial orchards within a 5 km radius. In those areas, practices adopted include monitoring the insect vector, ground or drone spraying, replacing citrus plants with other fruit trees and eradicating lemon sprouts in areas that were once orchards.
With all these actions, the loss of fruit-bearing area at Cambuhy was nine times lower than the regional average.



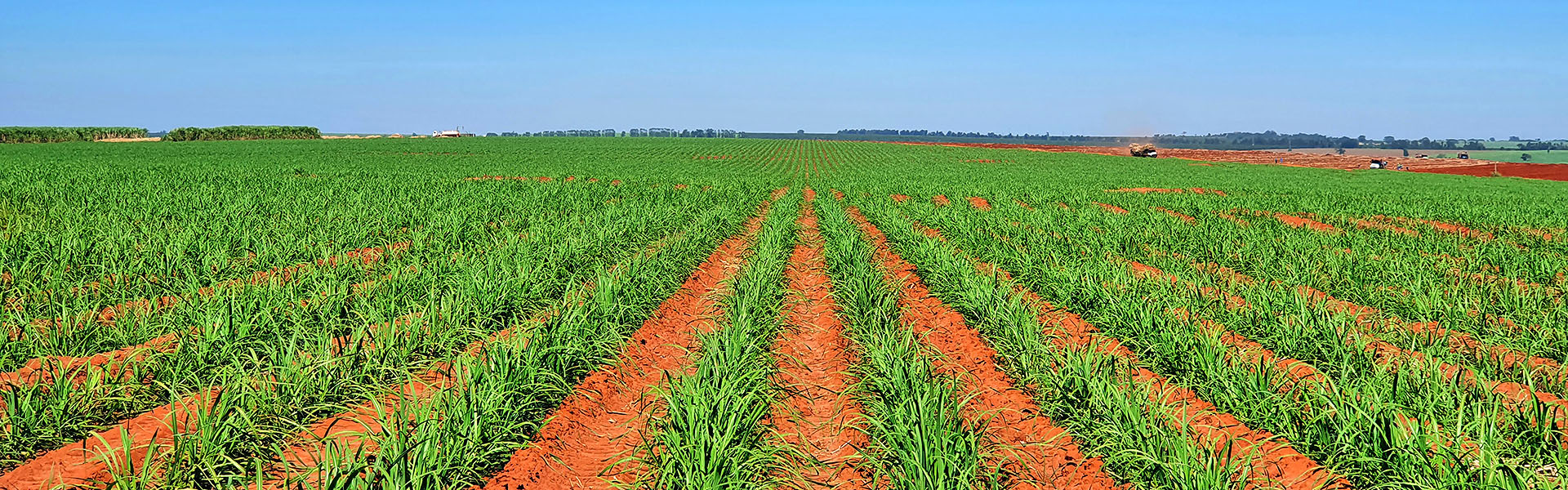
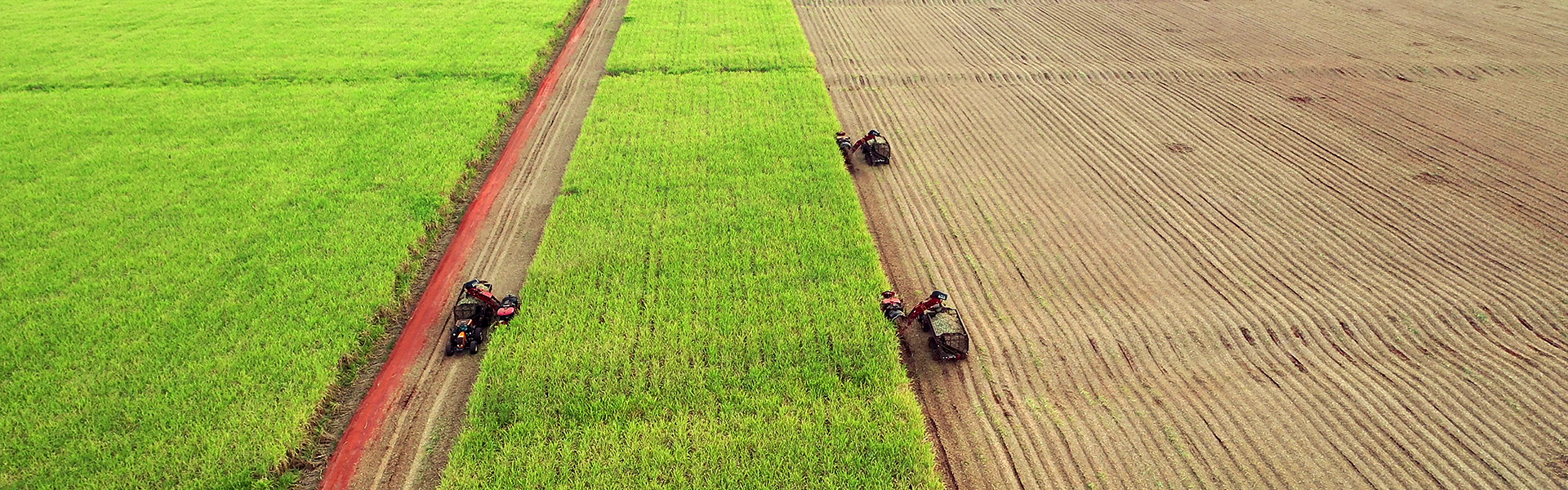
 Sugar cane
Sugar cane

SUGARCANE: AN INCREASINGLY RELEVANT CROP AT CAMBUHY
The sugarcane crop is recent at Cambuhy Agrícola but already occupies nearly 40% of its production areas, with impressive results in terms of yield, representing a 57.2 percent increase above the average for the state of São Paulo. In this sector, Cambuhy is a sugarcane supplier, and therefore its activities range from establishing nurseries and stands in the field to overseeing harvest, which is carried out by the industry. The activities carried out by Cambuhy are detailed below:
– Sugarcane nurseries [implementation of variety banks – pre-sprouted seedlings (PSS), nursery management, multiplication/replication of varieties];
– Planting (furrowing, closing of furrows, quality distribution of sugarcane billets);
– Phytosanitary control of stand establishment and production areas (monitoring of pests and diseases, chemical control applications, release of the biological control agent Cotesia flavipes);
– Cultural practices in the stand establishment and production areas (fertilization and soil amendment, weed management, management and maintenance of the sugarcane field);
– Harvest quality monitoring (harvest control, quality monitoring, harvest loss assessment).



